The majority of these tests focus on examining a person’s nervous system in addition to their muscular system. Many of these tests incorporate the drawing of blood to test things like vitamin levels and nutrition as well as liver and enzyme testing. More than half of liver patients experience neurocognitive impairments.” Loyola University Health System. Consequently, infections such as pneumonia and sepsis can increase a person’s risk for dementia.12 So if you have alcohol-related dementia, they can potentially worsen your condition. Today these two symptoms–amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles–remain defining marks of Alzheimer’s disease. If you are concerned that you or a loved one may be exhibiting signs of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome, contact a mental health professional today. Some studies have suggested that one or two units a day – perhaps a small glass of wine – could be protective.
In comparison, someone with dementia will slowly forget how it’s like to perform basic activities. They can put you at risk for falls, motor vehicle accidents, and other incidents that may result in traumatic head injuries — such as getting into fights.
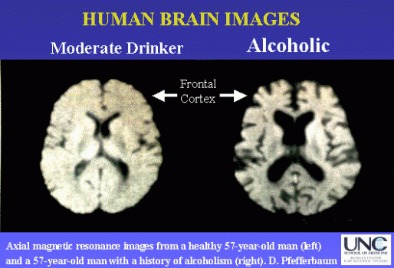
Through proper detox, abstinence, and a healthy diet, brain scans show some effects of heavy drinking can be undone. Alcohol treatment medications like Acamprosate and Naltrexone may be prescribed to block the effects of a relapse or reduce alcohol cravings.
Dementia, Alcoholism, And Balance Issues
Recent research indicates that alcohol plays a much larger role in early-onset dementia than previously thought. Heavy drinking comes along with a host of other factors that increase dementia risk, including risk-taking behavior, mental illness, lower levels of education, and physical health concerns. The longer someone spends abusing alcohol, the higher their risks are for developing dangerous chronic health conditions. On the contrary, early intervention of excessive drinking can prevent the development of certain hazardous and distressing physical and mental health conditions brought about by excess drinking.
If Wernicke encephalopathy is suspected, a person must get immediate medical treatment, typically consisting of high doses of thiamine and other B vitamins injected slowly into a vein. With timely treatment, most symptoms of this condition can be reversed within a few days. If Wernicke encephalopathy is left untreated or is not treated properly or rapidly, some people may have permanent brain damage, and very severe cases can even lead to death. Blood tests can show blood alcohol levels, markers of liver damage caused by alcoholism, and levels of thiamine. Your loved one will likely also need assessments that measure thinking and memory skills and screening for depression and other mental health conditions. Quitting drinking will prevent additional loss of brain function and damage.
The Alzheimer’s Association has counseling available for family members whose loved ones have alcohol-induced dementia. Seeking counseling for yourself is one thing in this situation that you can control. Upon further investigation, we learned that many in-patient addiction rehabilitation centers require that participants are healthy enough to engage in the treatment process.
The differing elements of drinking patterns as well as difficulties gaining an accurate self-report of past drinking have further complicated attempts to link drinking levels to later cognitive impairment. Estimates of past drinking habits of individuals diagnosed with ARD have included up to 60 years of drinking , although there is significant variability in length and severity of drinking .
Treatment Options For Excessive Alcohol Use And Abuse
Alcohol has been shown to decrease acetylcholine levels, reducing its synthesis and release. Improvement of cognitive function in alcoholics after abstention from alcohol suggests that the cognitive deficits may reflect neurochemical alterations rather than neuronal loss . Alcohol-induced cholinergic receptor losses in alcoholics with AD may contribute to the clinical symptoms of dementia. Alcohol does not appear to accelerate the AD process but instead induces its effects on the cholinergic system, independent of the cholinergic deficits caused by AD .
Use of this website is conditional upon your acceptance of our User Agreement. Overall, patients with alcohol dependence, or AUD, often lack insight into their condition, are ashamed, isolated, and, in many cases, lack access to proper healthcare.
Get Inpatient Alcohol Addiction Treatment Now
When too little thiamine is present in the body, brain cells cannot create enough energy to properly function. Wernicke’s encephalopathy can cause damage to various parts of the brain and can be deadly if not treated promptly. Patients with cognitive impairment also face difficulties in several factors involved in management.
Oslin refined the diagnostic criteria for ARD by including duration and severity of alcohol consumption and a minimum abstinence time, for a ‘probable’ diagnosis of ARD to be considered. He expected this classification would bring more clarity and stimulate further research in this area . Even till now, only a few studies have adopted these criteria and they still need research for being conclusive (13-15). Even in the short term, alcohol affects areas of the brain controlling cognitive and motor functions, causing them to slow down.
The study, which used the French National Hospital Discharge database, looked at more than a million people diagnosed with dementia between 2008 and 2013. At North Jersey Recovery Center, we strive to make your addiction treatment experience as comfortable as possible. But, at North Jersey Recovery, we design personalized treatment plans to give you the best chance of recovery. At Granite Recovery Centers, we want to provide accurate information about health and addiction so that our readers can make informed decisions.
As we’ve noted above, an alcohol use disorder fundamentally changes the way certain key areas of the brain function. As the brain and body become more habituated to the presence of alcohol in the body, it becomes more difficult for a chronic drinker to quit drinking.
This correlates with current neuroimaging evidence of at least partial structural and functional recovery from alcohol-related brain damage if abstinence is maintained. According to an animal study, the effects of thiamine deficiency are more persistent as compared to the effects of persistent ethanol exposure . Executive function, working memory, perceptual and motor impairments commonly endure following short-term abstinence, probably a reflection of compromised fronto-cortico-cerebellar functional networks .
See also, our primer on MAT for AUD and a Q&A on short-term addiction treatment with NIAAA Director George F. Koob. As anyone who’s ever had to interact with a loved one with dementia knows, these difficulties can change someone you’ve known your whole life into a person you no longer recognize. In WKS, an initial severe neurological syndrome may leave in its wake the condition called alcohol amnestic disorder. This syndrome, also known as Korsakoff’s psychosis, is characterized by profound difficulty making new memories. Multiple alcohol-related cognitive syndromes have been described, of which the two most important are alcohol-related dementia and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome .
Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative brain disorder characterized by a progressive loss of memory and other detrimental cognitive changes as well as lowered life expectancy . Aside from the substantial personal costs, AD is a major economic burden on health care and social services (Ernst and Hay 1994; Leon et al. 1998). Oslin proposed alternative clinical diagnostic criteria which were validated. B. The cognitive deficits in criteria A1 and A2 each cause significant impairment in social or occupational functioning and represent a significant decline from a previous level of functioning.C. The deficits do not occur exclusively during the course of a delirium and persist beyond the usual duration of substance intoxication or withdrawal.D.
- At the same time, alcohol is not a direct cause of this syndrome as much as brain cell damage.
- Editorial StaffThe editorial staff of American Addiction Centers is made up of credentialed clinical reviewers with hands-on experience in or expert knowledge of addiction treatment.
- While alcohol is best known for the damage it can cause in the liver and kidneys, heavy drinking and dementia have also been linked.
- In addition, getting back on the right track from a health perspective can help as well.
Damage to neurotransmitters slows communication between different areas of the brain and reduces energy levels. The Hypothalamus and the Pituitary work together to link the nervous system to the endocrine system. This region of the brain both stimulates and inhibits key hormonal processes in order to maintain the body’s internal balance.
One study pointed to common symptoms of “peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, sparing of language,” while another noted difficulties with “visuospatial functions, memory, and executive tasks”. Crucially, both of these studies acknowledge the possibility for partial recovery with sustained abstinence from alcohol. Cognitive and behavioral changes specific to ARD have received limited investigation. However, the ARD groups had poorer performance on visuospatial measures, including clock drawing and copying tasks.
Treatment providers can connect you with programs that provide the tools to help you get and stay sober. How COVID-19 Has Impacted Alcohol AbuseAs the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the numbers of alcohol abuse have continued to rise, causing concern across America. Even with the support of your local Alzheimer’s Association, helping someone with alcohol-induced dementia is a challenge. The first problem is the most glaring, and that’s the addict themselves.
If you or your loved one is experiencing cognitive effects from alcohol abuse, detoxing and achieving lasting abstinence may be the only way to mitigate or reverse the damage. From medical detox from alcohol to outpatient programs, our compassionate and experienced professionals are here to help.